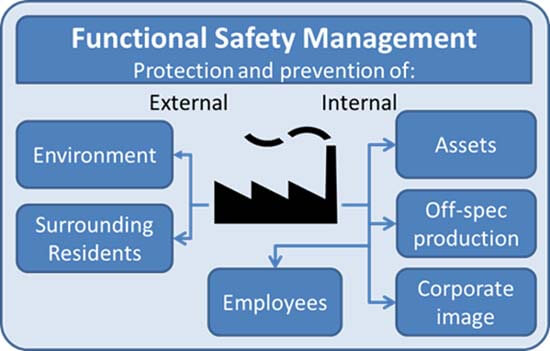
The demand on protection of humans and environment from an unavoidable process hazards is continuously growing and this in turn necessities the use of control systems with functional safety .So what does Functional safety means?
Functional Safety: it relates to the part of overall safety that depends upon the correct operation of an electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety instrumented system, SIS. The requirements for such a SIS are defined in the IEC 61508 group of standards.
IEC 61508 standard: is a ‘generic’ standard, intended to satisfy the needs of almost all process industries. It sets out the requirements for ensuring that systems are designed, implemented, operated and maintained to provide the required safety integrity level (SIL).The principles documented in the standard are accepted internationally.
SIS: A SIS is a Safety Instrumented System and it plays a major role in providing a protective layer around industrial process systems. It’s also called as emergency or safety shutdown system or a safety interlock. It’s mainly designed is to take process to a “safe state” when a safe level threshold is exceeded.
SIF: A Safety Instrumented Function (SIF) is a safety function with a specified Safety Integrity Level which is implemented by a SIS in order to achieve or maintain a safe state
SIL: SIL means Safety Integrity Level. A SIL is a measure of safety system performance, or probability of failure on demand (PFD) for a SIF or SIS. There are four integrity levels associated with SIL. The higher the SIL level, the lower the probability of failure on demand for the safety system and the better the system performance.
While SIL is a measure of process’ inherent safety, an important factor used in calculating SIL ratings is the product’s reliability. In order to determine if a product can be used in a given SIL environment, the product must be shown to “BE AVAILABLE” to perform a dedicated task at some predetermined rate. Considerations taken into account when determining “AVAILABIITY” include MTBF, MTTR, and PFD.
PFD: The effectiveness of a SIS is described in terms of “the probability it will fail to perform its required function when it is called upon to do so.” This is its Probability of Failure on Demand (PFD)
MTTR: Mean Time To Repair . It is the average time required to troubleshoot and repair failed equipment and return it to normal operating conditions
MTBF: Mean Time Between Failure. It refers to the average amount of time that a device or product functions before failing.
Reliability: The probability that an item will perform a required function, under stated conditions, for a stated period of time.
Availability: It can be defined as “The proportion of time for which the equipment is able to perform its function” Availability is different from reliability in that it takes repair time into account. An item of equipment may not be very reliable, but if it can be repaired quickly when it fails, its availability could be high.